Introduction
When we learn about types of computers, we can learn about computer groups and many more. You can know about computer hardware and you can easily choose the best. It can help you for computer security. then you can use them like professionals do.
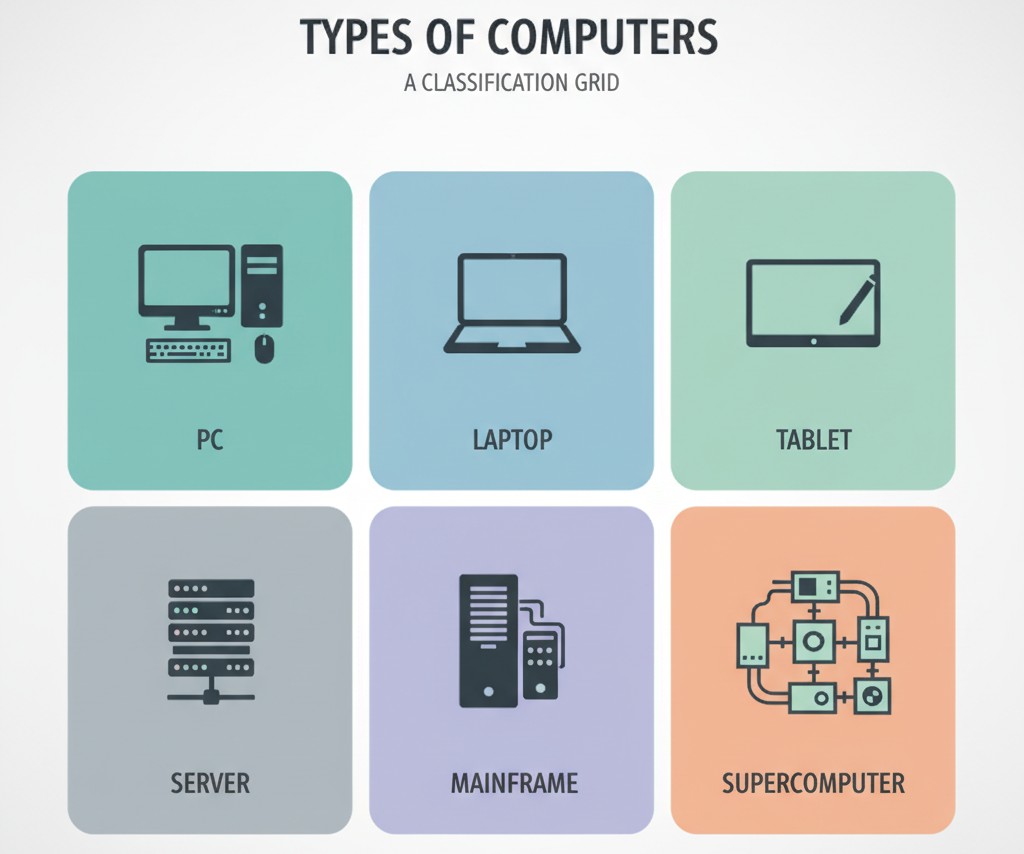
Classification by Data-Processing Method
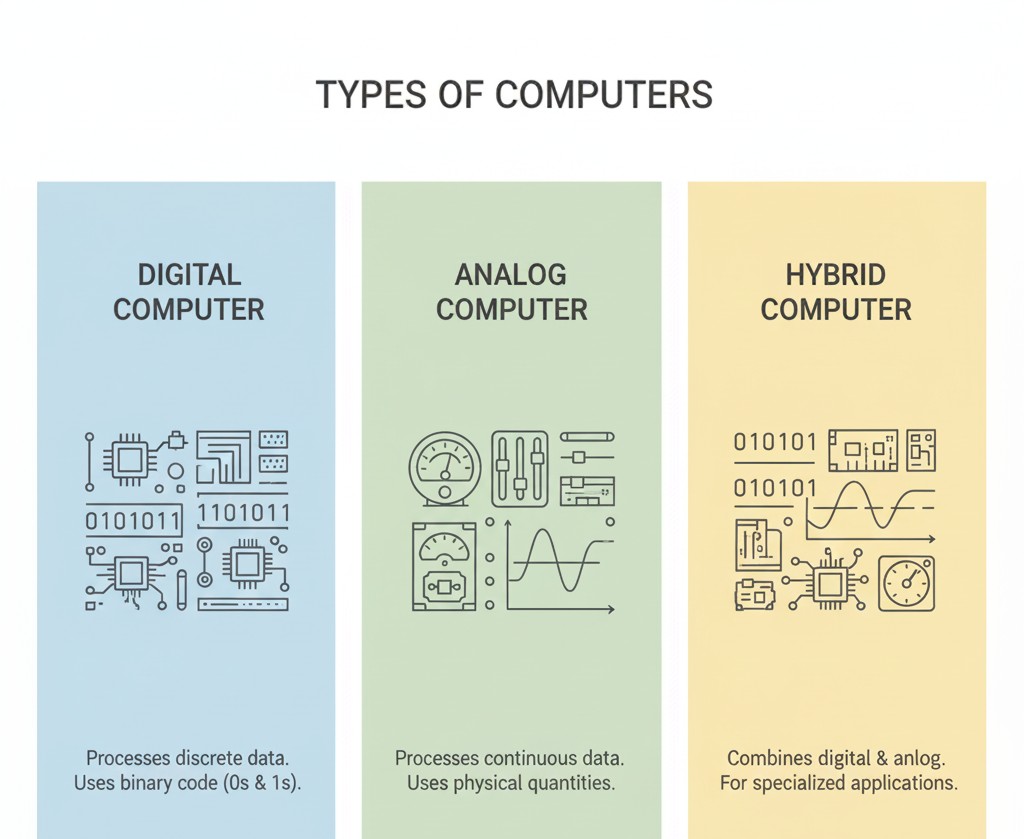
We can find analog computers, digital computers, and hybrid computers. Each computer works in different ways.
Analog Computers
The analog computer mainly works with signals. It uses voltage, temperature, or speed. This computer works in the signal process by using signals that’s why it is used in real life.
Examples
We can see at a car speedometer. When the speed meter goes up means it’s high and when it goes down means it’s low.the thermostat uses temperature signals in analog form.
Old scientific machines use this signal to solve math problems. Some flight simulators like old models use analog signals. They show electric waves and some meters as airplane signals.
Pros
Analog computers show real signals and It’s very useful for real life use.
Cons
It have low store option and some time it make signals noisy. That’s why it make complex to use.
Digital Computers
A digital computer reads data in the form of 0 and 1. This programme is common nowadays. Nowadays personal computers are everywhere. It is also used in smartphones, laptops and to connect us to the internet.
Digital computers use many different parts of computer hardware to operate. The CPU handles tasks, and the memory helps store and load data. This system is very easy to update and to do daily life tasks.
Hybrid Computers
A hybrid computer uses a mix of analog signals and digital data. A common example is a medical monitoring system. It reads body signals and shows the final data on a digital screen.
Many specialized systems use hybrid computers. You can’t find them in public these mainly use in labs, hospitals, and research rooms.
Classification by Purpose
Some computers are made for fixed work and some are made for multi work purposes.
General-purpose Computers
A general-purpose computer can do multiple jobs. It can run a lot of software for multiple tasks. PCs, laptops, and workstations are doing this. People can write, browse the internet, graphic design and many more.
This kind of computer depends on computer hardware. Parts like the CPU, memory, storage, and GPU help them run tasks smoothly. This kind of computer is used in school, college and personal uses.
Special-purpose Computers
A special-purpose computer made for only special reasons. It cannot run other tasks and can only do one job. For example you can see traffic light systems, microwaves, and washing machines.
They just do a job which is fixed for them. They simply run in the background silently and do their job which they were made for.
Classification by Size / Performance
Computers made by different parts and for different purposes. Nowadays computer making companies are trying to make that kind of machine which can easily carry and use anywhere.
On the other hand, many computers are made for industrial use. These kinds of computers are huge and work in large capacities. Size can be matter for different job and task
Microcomputers / Personal Computers (PCs)
Microcomputers are very small systems made for personal use only. They run on a single microprocessor and we can use at home or work.
Varieties
- Desktops – used on a desk and good for regular work or gaming.
- Laptops – light, portable, and easy to use anywhere.
- Tablets – touchscreen devices like smartphones for simple tasks and entertainment purposes.
- Single-board computers (SBCs) – tiny computers on one circuit board like Raspberry Pi.
Advantages & Uses
Microcomputers are easy to use and fit for your daily work. People mostly use them for browsing, studying, office tasks, and content work.
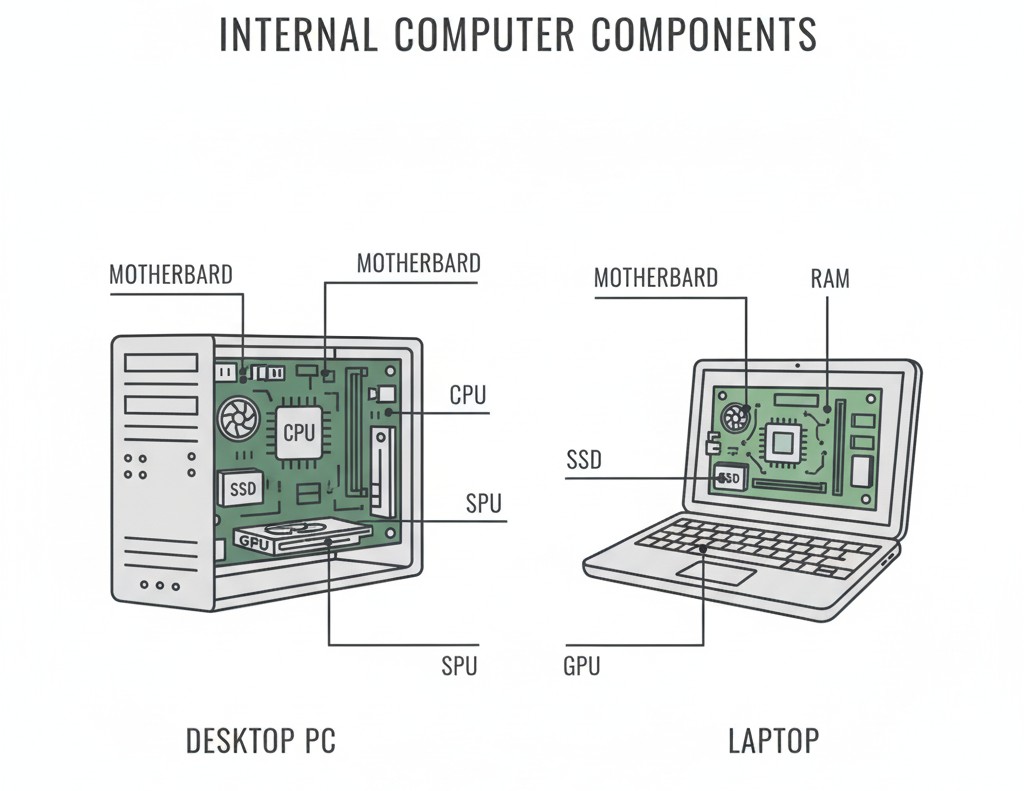
Main Parts Inside a PC
Computers run by many computer parts. Some are main like:
- Motherboard – Connects everythings.
- CPU – handles instructions and tasks.
- RAM – short-term memory for running programs.
- Storage – HDD or SSD to save files and software.
Computer Security on PCs
PCs store and maintain your personal and work data. You need to protect your PC for your personal information and data. If your PC is protected then your personal data and information also work data is protected.
You can protect it by using antivirus, installing updates, and avoiding unsafe downloads and unsafe browsing can reduce risks. You have to always be alert because scammers and hackers are always trying to get your data.
PC Maintenance
Adding more RAM or replacing the storage with an SSD can improve your PC’s speed. Always clean dust from your PC and install all software for smooth work.
Mainframe Computers
Mainframes are very large and very strong computers. They can support thousands of users at the same time.
Where Mainframes Are Used
Banks and government offices depend on mainframes. Airlines and many others large companies use them for nonstop operations.
 Reliability & Security
Reliability & Security
Mainframes are made to run long hours non-stop. They also have strong security and backup features. They are maintained by well experienced and trained teams. Their design focuses on stability and safe data handling.
Supercomputers
Supercomputers are the fastest computers available in the world. They are built to solve the most extremely tough problems.
What Supercomputers Do
Experts use them for weather reports, climate studies, and scientific research.
They can handle huge simulations that normal computers cannot control.
Famous Supercomputers
Many known systems are listed in the TOP500 ranking. These computers are famous for very high processing speed.
Other Specialized Computer Types
Some computers are built only for special roles. They are used where normal PCs are not enough to operate.
Server Computers
A server is a computer that provides services to other devices. It stores data, runs websites, and manages others networks.
Types of Servers
- Rack servers – placed inside large racks in data centers.
- Blade servers – thin units that fit in compact enclosures.
Where Servers Are Used
Servers handle websites, databases, file storage, and email systems. They help companies run online and internal operations.
Security & Maintenance
Servers always need strong network protection. They run all day and must stay in a stable position. Monitoring keeps the system healthy and safe.
Workstations
Workstations are strong PCs used for professional work. They give a higher speed that can’t be given by a common home computer.
Typical Uses
Engineers, designers, and video editors usually use them. They handle CAD work, editing, and 3D work smoothly.
Hardware Inside
Workstations often include powerful CPUs and GPUs. Can use ECC RAM for better stability.
Embedded Systems / Embedded Computers
An embedded computer lives inside a device and controls its functions. It is not used like a normal PC.
Examples
- Smart home gadgets
- IoT devices
- Smart TVs
- Car systems
- Medical equipment
Challenges
They run for long periods without many updates. Security and firmware maintenance are very important.
Single-Board Computers (SBCs)
An SBC is a full computer on one small board. All the main parts in a tiny small space.
Common Examples
- Raspberry Pi
- Arduino (used as a computing unit)
Uses
SBCs are helpful for learning and small projects. They are usually used in robotics and embedded work.
Hardware Parts
They use a microprocessor and basic ports only. Some models include onboard memory as well.
Key Components (Parts) of a Computer
Most computers have a few common parts. These parts give them how fast and smooth the system will run.
- CPU – handles tasks
- RAM – stores active data
- Storage (HDD/SSD) – keeps files
- Motherboard – connects everything
- GPU – manages graphics
- Power supply – gives power
- Input/output devices – keyboard, mouse, monitor etc.
Computer Security Considerations
Security needs for every type of computer. All systems store your data or run tasks that must stay safe.
Common Threats
- Malware
- Hacking attempts
- Unauthorized access
- Physical damage
- Best Security Practices
- For PCs and Laptops
- Install antivirus.
- Keep software updated.
- Avoid unsafe programs.
- Use strong passwords.
Maintenance & Upkeep of Different Types of Computers
If you take care of your computer it will be fast and stable. It also helps you avoid unexpected problems later. You need to care about hardware and software. You have to clean the dust which can affect your PC’s cooling system.
You have to avoid unsafe browsing and download files from unwanted sites. Upgrading RAM or switching HSS to SSD can help when you are feeling the device is slow.
How to Choose the Right Type of Computer for Your Needs
It depends on your daily work basis. Which kind of work you do. Like if you want to graphic design you need a strong PC. If you need only for office work you can easily choose laptops.
Now comes industrial and business use. You need powerful computers for this. So it depends on your work type.
Conclusion
So first check your work and then check your budget. Before buying any computer try to clear your need and focus on work. Then choose any kind of model which has specifications for doing your tasks.
FAQs
1. What are the main types of computer?
There are mainly types of computer analog, digital, and hybrid computers.
2. How do digital, analog, and hybrid computers differ?
Digital computers use binary data like 0 and 1. Analog and hybrid computers work with real-world signals.
3. What is a supercomputer used for?
A supercomputer can do very heavy tasks. It is used in research, weather work, and high performance tasks.
4. What is the difference between a mainframe and a minicomputer?
Mainframes can control huge workloads.
5. How is a workstation different from a regular PC?
A workstation has stronger computer parts. It is built for work like editing, 3D work, or coding.